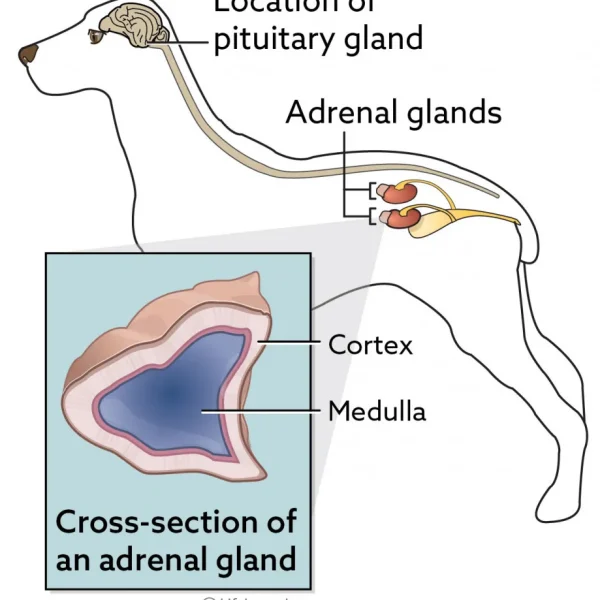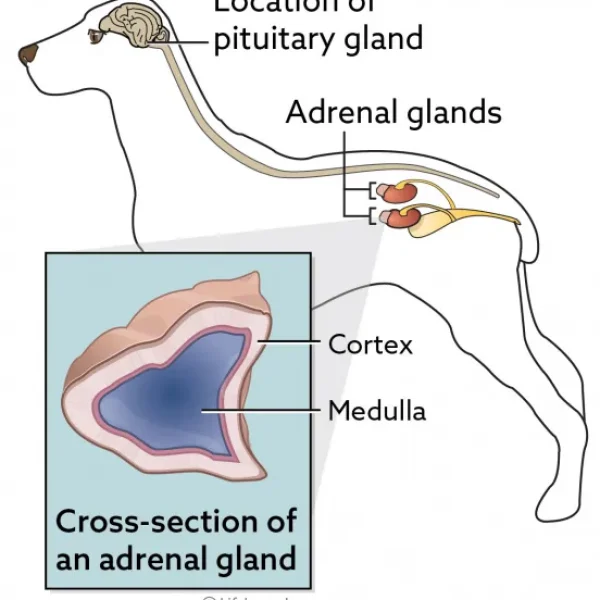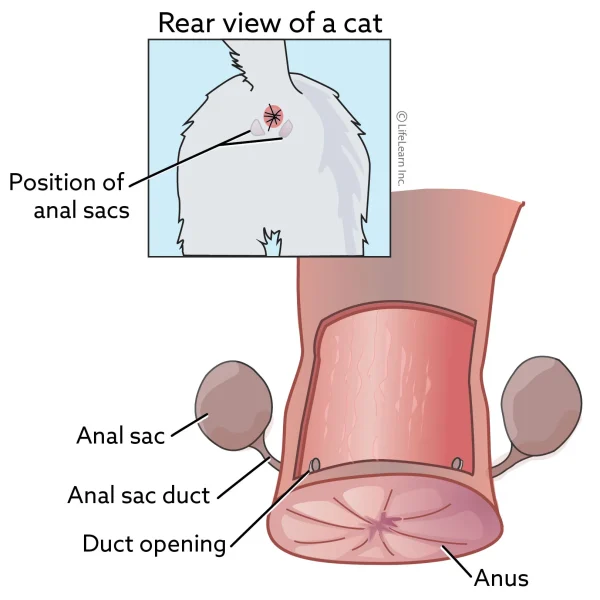
Anal sac tumors grow quickly and have a moderate risk of spreading to other parts of the body. Depending on the tumor’s size, your pet could develop signs of straining to defecate or produce thin ribbon-like stool. An increased calcium level in the blood is consistent with anal sac tumors, which can cause other signs and result in kidney failure. The best and most well-described local treatment for the primary tumor is surgery. Radiation and chemotherapy may be considered if there is evidence of spread.