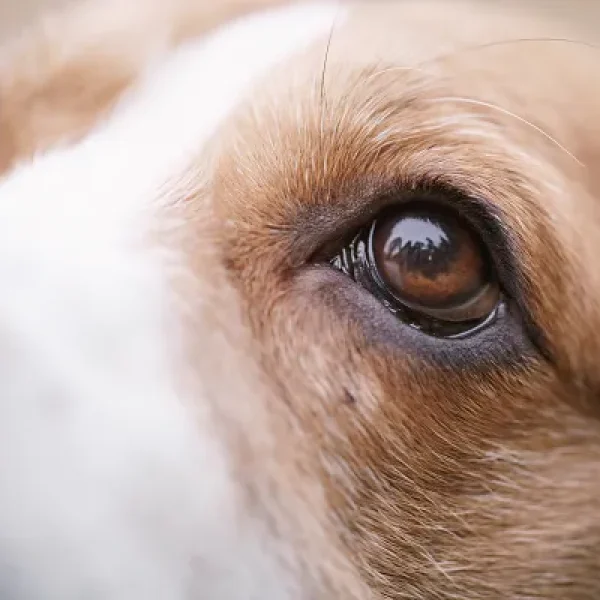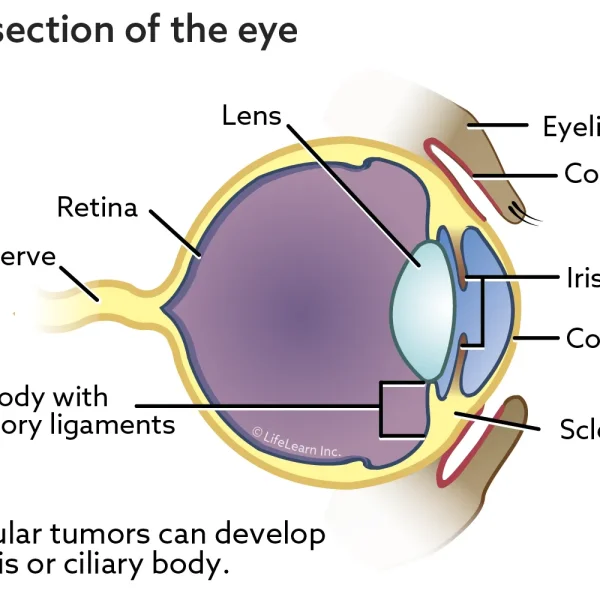
Primary intraocular tumors, aside from melanoma, are relatively uncommon. There are many different types of primary tumors, including ciliary body adenoma and adenocarcinomas, uveal schwannomas of blue-eyed dogs, feline post-traumatic ocular sarcomas, and iridociliary adenomas and adenocarcinomas. When an intraocular tumor is suspected, a referral to a veterinary ophthalmologist may be recommended. Diagnosis is usually via an abnormal ophthalmic examination and/or ophthalmic ultrasound. Surgery is often recommended, especially if the pet has symptoms that reduce quality of life. The risk of metastasis is related to the type of tumor.