Expanding Glues

All glues containing isocyanate and diisocyanate can expand. Pets exposed to a very small amount of wet or liquid expanding glue may consume enough product to be problematic. Foreign body obstruction due to a mass of expanded glue in the stomach is the most common outcome in dogs ingesting expanding wood glues. After abdominal X-rays confirm the presence of a glue mass and obstruction, surgery is required to remove the mass, or endoscopy in mild cases. The prognosis for recovery from expanding glue ingestion depends on the removal of the mass.
Epilepsy in Dogs
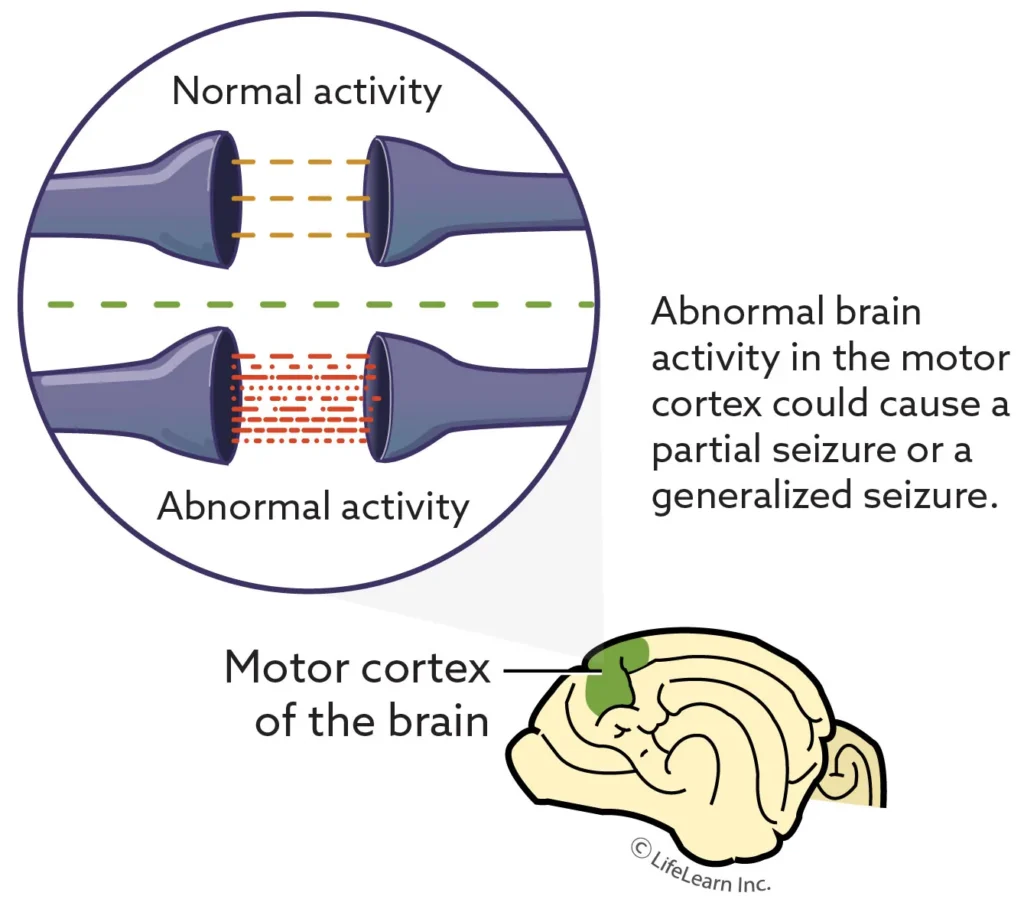
Epileptic seizures in pets are a diagnosis of exclusion and may be found in any dog but there may be some breed predispositions that are more common. The cause is often unknown. A variety of medications are available to help control the seizure activity if an underlying cause is not found.
Emergencies in Dogs
There are many types of emergencies, but initial care is similar: stay calm, keep your dog warm and quiet, contact your veterinarian, and get help to transport your pet to a veterinarian. Common emergencies are described including gastric dilatation and volvulus (GDV), acute hemorrhagic diarrhea, anaphylaxis, automobile injury, seizures, respiratory distress, eye injury, eclampsia, heatstroke, heart failure, toxin ingestion and collapse.
E-Cigarettes and Pet Safety

E-cigarettes are battery-operated devices used to create and inhale an aerosol composed of nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals. If a companion animal ingests an e-liquid, signs of nicotine poisoning occur rapidly. The nicotine associated with e-cigarettes, even without tobacco, poses a serious health threat to dogs and cats.
Melioidosis in Dogs

Melioidosis is a bacterial infection that is typically associated with tropical regions. The bacteria that causes melioidosis, Burkholderia pseudomallei, is usually found in soil and water. The clinical signs of this condition, along with transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis, are outlined in this handout.
Lyme Disease in Dogs

The bacterium that causes Lyme disease can be transmitted to dogs through the bite of an infected tick, most commonly the deer tick (black-legged tick), which is found in the midwestern and eastern United States and throughout Canada. The disease typically causes pain and swelling in the affected dog’s joints along with decreased appetite and fever. The kidneys are sometimes affected, in which case the disease is often fatal. Diagnostic testing, treatment, and ways to prevent Lyme disease in your dog, including instructions for tick removal, are explained in this handout.
Leptospirosis in Dogs

Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease of dogs and other mammals that primarily affects the liver or kidneys. The bacteria (Leptospira) that cause leptospirosis thrive in water. Infected or recovered carrier dogs may act as a source of the infection. Antibiotics such as penicillin, ampicillin, and amoxicillin, are reasonably effective against the acute stages of leptospirosis if started early, although most affected dogs require intensive care in the veterinary hospital. This disease can be transmitted to humans.
Leishmaniasis in Dogs

Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by a protozoan parasite transmitted by sandflies and is most commonly seen in the Mediterranean, Middle East, and South and Central America. It has been reported in some parts of the United States. Clinical signs include hard skin nodules, weakness, decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and more. Diagnosis is based on travel history, clinical signs, and diagnostic testing. The goal of treatment is to resolve clinical signs. Prognosis is guarded to grave depending on the severity of the disease.
Internal Parasites in Dogs

This handout outlines internal parasites in dogs. Included are parasites of the gastrointestinal tract (roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, and tapeworms), as well as parasites of the circulatory system (heartworm). How each of these parasites can affect your dog and what you can do to prevent or treat infection are all explained.
Indoor Dogs and Infectious Disease

Vaccinations are important to prevent serious illness in dogs. Even dogs that spend all their time indoors should be vaccinated. Some viruses can be carried into your home on inanimate objects such as shoes and clothing, therefore infecting your dog without him coming into contact with another animal. Your veterinarian is your most important resource in determining what vaccinations you need to give your dog to keep him protected.

