Ear Canal Tumors
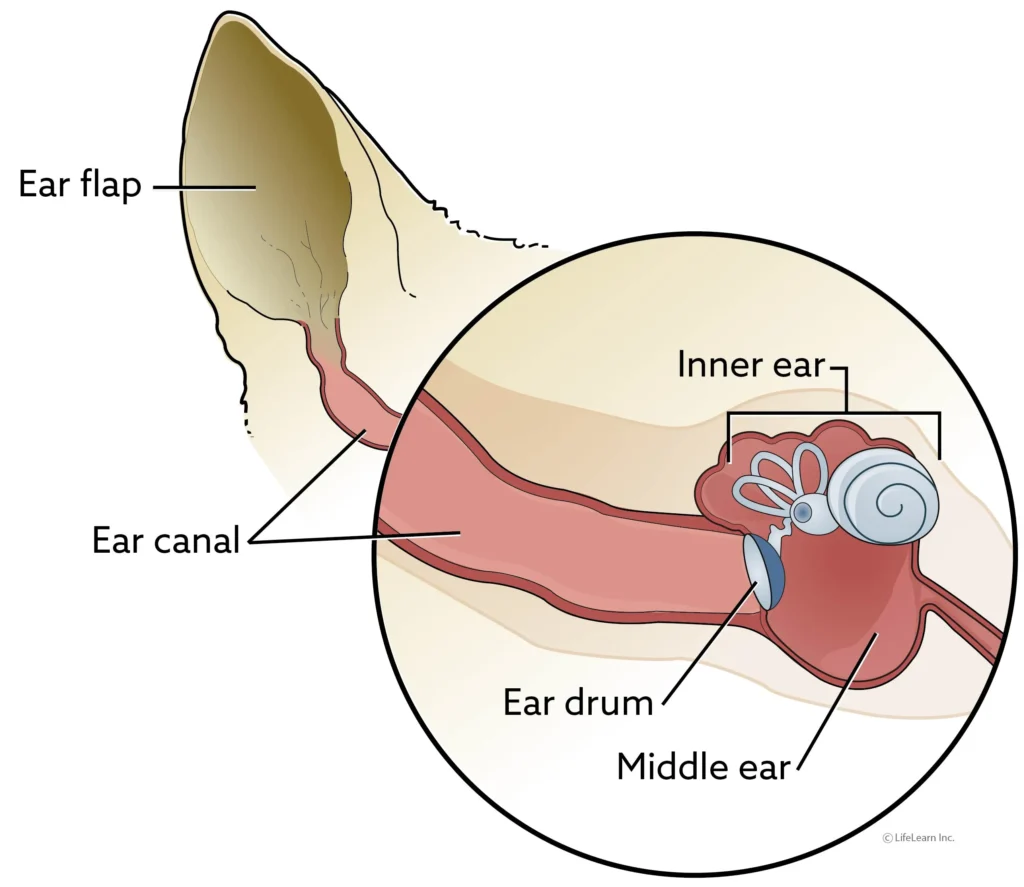
Ear canal tumors are abnormal growths that can develop from any part of the ear canal (the skin, the glands of the skin that produce earwax and oil, and the underlying connective tissues, muscles, and bones). Initially, these tumors may appear as one or more pink, white, or purple nodular masses in the ear canal. If benign, they may grow to a certain size and may or may not be problematic. If malignant, they may grow, ulcerate (break open) and bleed, and nearly always become infected, causing recurrent or chronic ear infections. The treatment of choice for ear canal tumors is surgical excision.
Cytology, Biopsy, and Histopathology
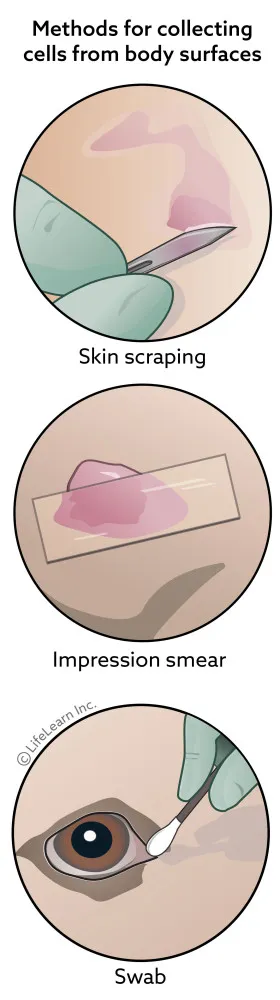
Collecting tissue samples for cytology or histopathology allow a pathologist to often give a diagnosis of the type of mass or tumor your pet has. Samples can be obtained by fine needle aspirate or biopsy, where a piece of the mass is cut out. Based on what the mass appears like under the microscope, the pathologist can often give a prognosis of how the tumor will behave.
Cutaneous Lymphoma in Dogs

Systemic lymphoma is a very common cancer in dogs, but the cutaneous form is quite rare. Current statistics suggest that cutaneous lymphoma accounts for only about 5% of canine lymphoma cases. The disease can present in a variety of lesions, including ulcers, nodules, red patches, and areas of hair loss and skin scaling. Because not very much is known about canine cutaneous lymphoma, there are no standard treatment protocols and the prognosis is poor.
Cutaneous Histiocytosis

Cutaneous histiocytosis is an uncommon condition in dogs. It is a non-cancerous increase in the number of reactive cells (histiocytes) caused by an immune system dysfunction. It generally manifests as multiple bumps and nodules confined to the dog’s skin. The clinical signs, diagnosis, and treatment of this condition are explained in this handout.
Cutaneous Histiocytoma in Dogs

A cutaneous histiocytoma is a common benign (harmless) tumor of the skin in dogs, typically younger ones. Their development, appearance, diagnosis, and treatment are explained in this handout.
Chondrosarcoma in Dogs

Chondrosarcomas arise from cartilage, which is a connective tissue primarily found where bones meet with joints, as well as at other locations in the body such as the nasal cavity, and ribs. Chondrosarcoma is the second-most common primary bone tumor in dogs. Canine chondrosarcoma most commonly affects the flat bones of the body, such as the ribs, skull, nasal cavity, and pelvis, although the limbs can also be affected. Aggressive surgical removal is typically recommended, although radiation therapy may also be used, depending on location of tumor. Metastasis may occur but is relatively uncommon.
Chemotherapy

Chemotherapy is the therapeutic use of chemical agents to destroy or inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells. Usually, chemotherapy is used when tumors are widespread or when there is significant or immediate risk of spread from the primary location. It is often used following the surgical removal of tumors. In some cases, chemotherapy is started prior to surgery. The side effects of chemotherapy are related to the effects of chemotherapy on normal -as well as cancerous- cells. The principal goal of cancer care in pets is to provide cancer control without reducing quality of life.
Chemodectomas (Aortic and Carotid Artery Neuroendocrine Tumors)
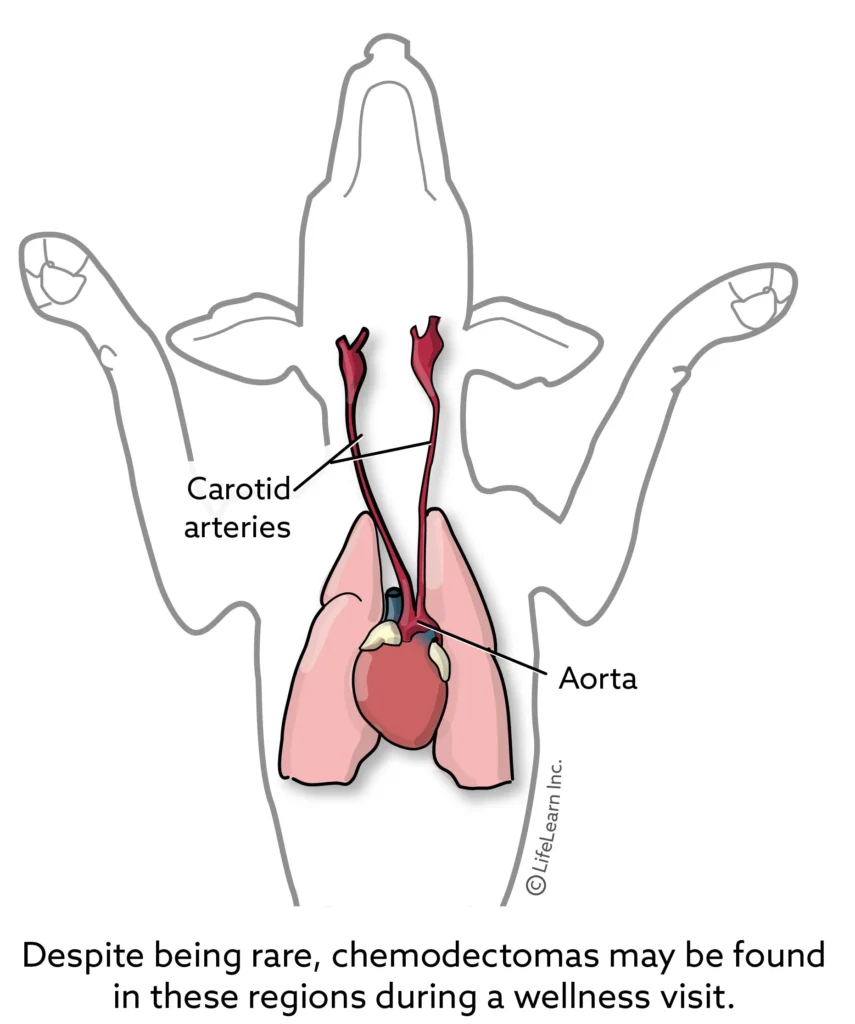
A chemodectoma is a type of tumor made up of chemoreceptor cells. Chemoreceptor cells detect chemical changes in the body and respond by regulating chemical or physical processes. These tumors are most often seen along one of the carotid arteries and the aorta. Brachycephalic breeds are more predisposed to these types of tumors, though they may occur in any dog breed. These tumors are usually locally aggressive, however, there are rare cases of metastasis to other organs, including the lungs, lymph nodes, and bone.
Benign Mammary Tumors in Dogs
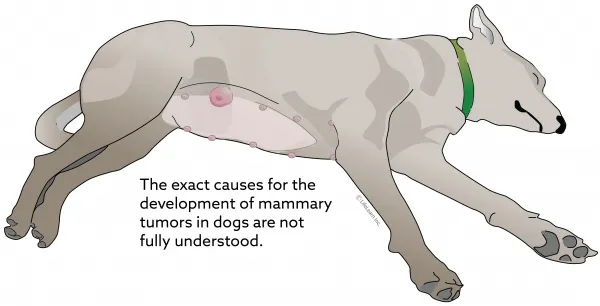
Mammary tumors develop due to abnormal reproduction of the cells that make up the breast tissue. They can be benign or malignant. The incidence of these tumors is related to hormone status, specifically whether a dog is intact or has had an ovariohysterectomy, age, and breed. Because dogs can have both benign and malignant tumors at the same time, surgical removal and histopathology of all tumors are very important.
Benign Fibrous Skin Tumors
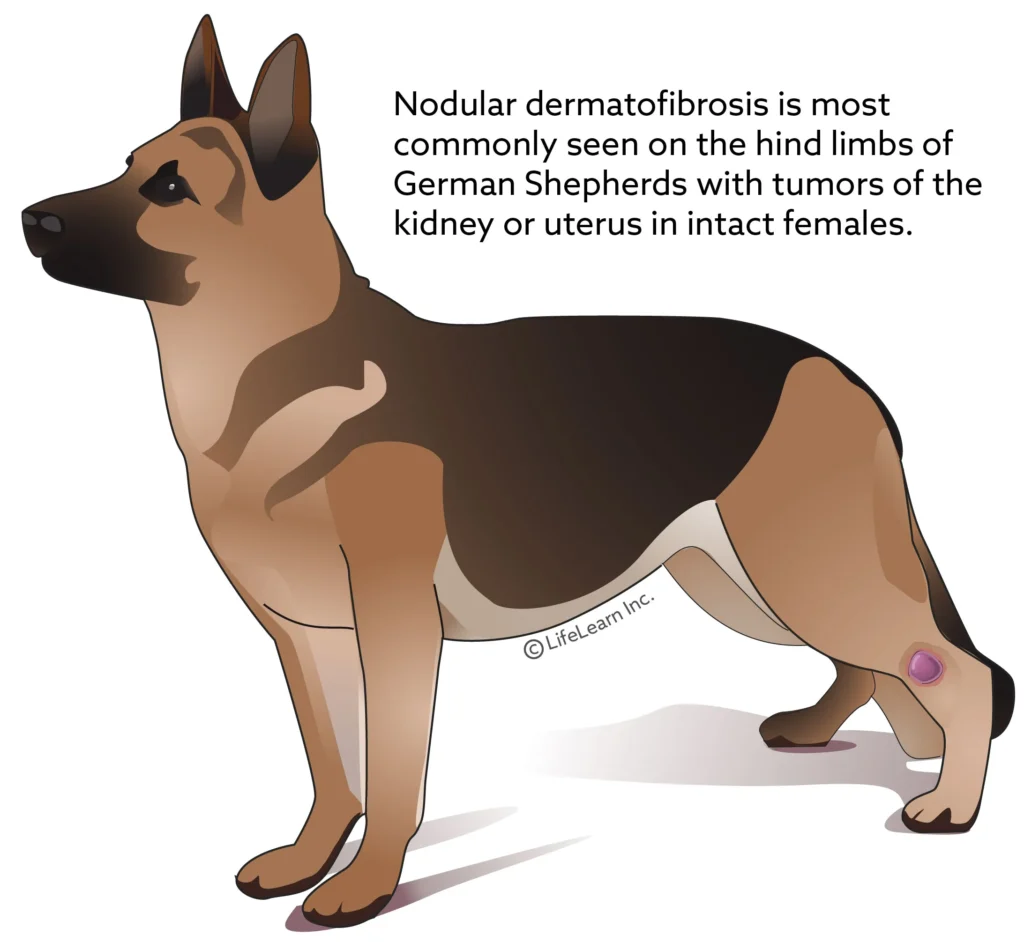
Benign fibrous skin tumors can go by many names and in many cases don’t need treatment. Surgical excision can be curative unless certain types are due to an underlying tumor elsewhere. The main focus in many cases is addressing underlying allergies or sources of pressure. To adequately diagnose these tumors, a biopsy and histopathology are usually necessary.
