Pregnancy and Labor in Cats

Breeding cats can be an extremely rewarding experience. However, before undertaking a breeding program, it is essential to understand what this involves, from the time of mating to the time of weaning. Pregnancy or gestation ranges from 60-67 days, averaging 63-65 days.
Polycystic Kidney Disease in Cats

Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited condition that causes multiple cysts (fluid pockets) in the kidneys. Persian cats and breeds with Persian bloodlines are most commonly affected. The clinical signs, diagnosis, genetic testing, and treatment options are explained in this handout.
Miscarriage in Cats
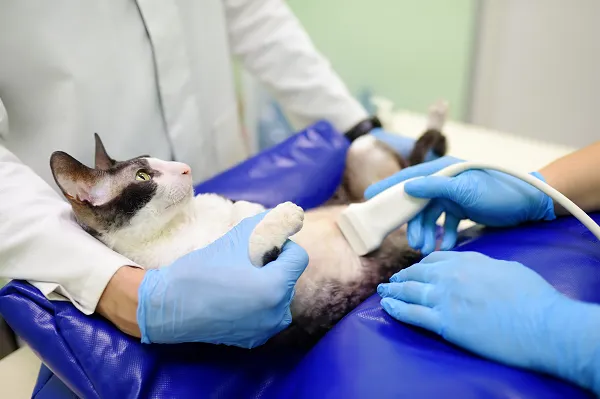
Miscarriage refers to the death of a fetus during pregnancy, with the most common cause being infection. It may also be caused by hormonal shifts or abnormalities. In many cases, there are no visible signs of miscarriage. If miscarriage is suspected, ultrasound is used to assess the pregnancy and determine whether the fetuses are alive. Finding a cause for the miscarriage, especially if that cause is a treatable condition, may improve outcomes in future pregnancies.
Mastitis in Cats

Mastitis is a term used to describe inflammation of a mammary gland (breast), most frequently seen in the postpartum period after a cat gives birth. In most cases, mastitis is caused by a bacterial infection. Trauma to the nipple or teat canal can allow bacteria to enter, traveling up into the mammary gland and creating a bacterial infection. Most cats with mastitis can be treated on an outpatient basis with oral antibiotics and pain medications, though severe cases may require hospitalization or surgery.
Infertility in Male Cats

Male infertility refers to the inability of a sexually mature tomcat (intact male cat) to impregnate a fertile female. This handout explains the possible causes of infertility in male cats as well as how they may be diagnosed and, when possible, treated.
Infertility in Female Cats

Infertility in a queen (an intact female cat) is defined as the inability to give birth to live kittens, despite appropriate breeding with a fertile male.This handout provides an outline of common causes of infertility along with how they are diagnosed and, when possible, treated.
Feeding the Pregnant Cat

Special attention needs to be given to a cat’s nutrition before and during her pregnancy to promote a healthy birth and healthy kittens. It is important to maintain a good body condition throughout pregnancy as her weight increases. A good quality kitten or all life stages diet is recommended during the entire pregnancy; ideally one evaluated using feeding trials. This diet is usually fed throughout the lactation period, but attention to body condition is essential here as well, and the diet may need to be restricted if there is a small number of kittens or the cat starts becoming overweight. Weaning is usually aided by feeding significantly less food for a few days while restricting access to nursing to decrease milk production.
Feeding the Nursing Cat
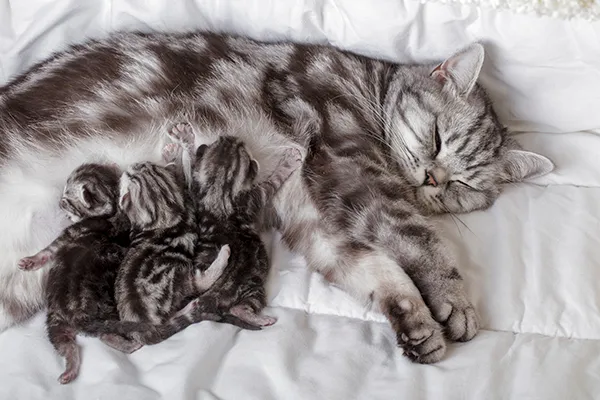

This handout discusses the need for ensuring your pregnant cat is receiving adequate nutrition to make sure both she and her kittens thrive during this time of increased demands on her body. Feeding and diet suggestions are provided.
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome in Cats

Chediak-Higashi Syndrome is a rare genetic disease of smoke-blue Persian cats. The condition affects how the body processes waste products, resulting in changes within the body’s cells and leading to abnormal pigmentation of the skin and coat. The condition can lead to eye abnormalities and problems with blood clotting, but most cats can have a normal lifespan with careful health monitoring.
Cesarean Sections in Cats – Post-Operative Instructions
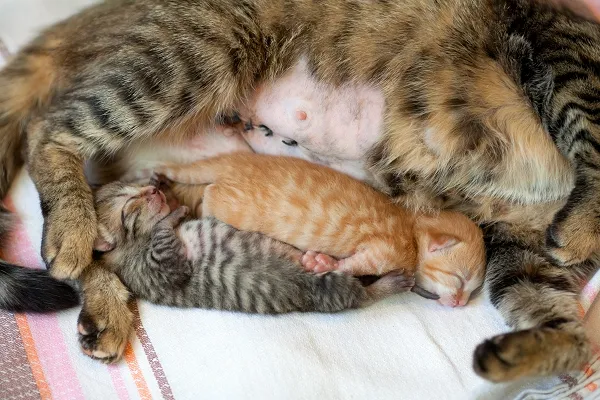

A cesarean section is a surgery to remove kittens from the uterus and is most commonly performed as an emergency procedure when there is difficulty with natural birth. During the immediate recovery period, the mother and kittens must be closely monitored and begin eating/nursing within a few hours. If you have any concerns about their health, you should immediately have your veterinarian examine the kittens and their mother.

