Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome in Cats

Brachycephalic airway syndrome refers to a particular set of upper airway abnormalities that affect brachycephalic cats. The most common sign of the condition is mouth breathing and, in the long term, the increased effort associated with breathing can put a strain on the cat’s heart. Surgery is the treatment of choice whenever the anatomical abnormalities interfere with a cat’s breathing.
Bowel Incontinence in Cats

Bowel incontinence is the loss of the ability to control bowel movements. There are two broad causes of fecal incontinence: reservoir incontinence and sphincter incontinence. In reservoir incontinence, intestinal disease interferes with the rectum’s ability to store normal volumes of feces. In sphincter incontinence, a structural or neurologic lesion prevents the anal sphincter from closing normally. Clinical signs, diagnostic testing, and treatment vary based on the underlying cause.
Blepharitis in Cats

Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid) can affect one or both eyes. The affected eyelid will usually be red, swollen, and itchy. Any condition that can cause irritation of the eyelids can lead to blepharitis. The numerous potential causes of this condition, along with the clinical signs, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis are outlined in this handout.
Anesthesia for Cats

Anesthesia is accomplished by administering drugs that depress nerve function. It is important that you fully understand what will happen to your pet, and that you understand the risks. Anesthetic monitoring in a veterinary hospital is like that found in any human hospital. With today’s anesthetics, many of which are reversible, your pet should be almost completely normal by the time of discharge.
Wellness Testing for Senior Cats

Regular wellness exams and laboratory testing are designed to detect hidden disease in older cats, allowing earlier intervention to manage or slow the progress of the disease. Typical testing in senior and geriatric cats includes complete blood count (CBC) that assesses the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets; a biochemistry panel that provides information about the organs, electrolytes, blood sugar, and proteins; urinalysis that assesses kidney function and can identify inflammation or infection in the urinary tract; thyroid testing to identify hyperthyroidism; and blood pressure assessment to identify hypertension.
Exercises to Improve Proprioception

Proprioception is the ability to know where your body is in space. This is what helps reduce falls and injury. Proprioception may be lost suddenly through spinal cord trauma, or it may be reduced with age, joint disease (osteoarthritis), or other orthopedic or neurologic disease. Some specific controlled exercises that can improve proprioception are discussed. Any exercise plan needs to be formulated by a veterinary rehabilitation therapist to avoid injury.
Retained Testicle (Cryptorchidism) in Cats
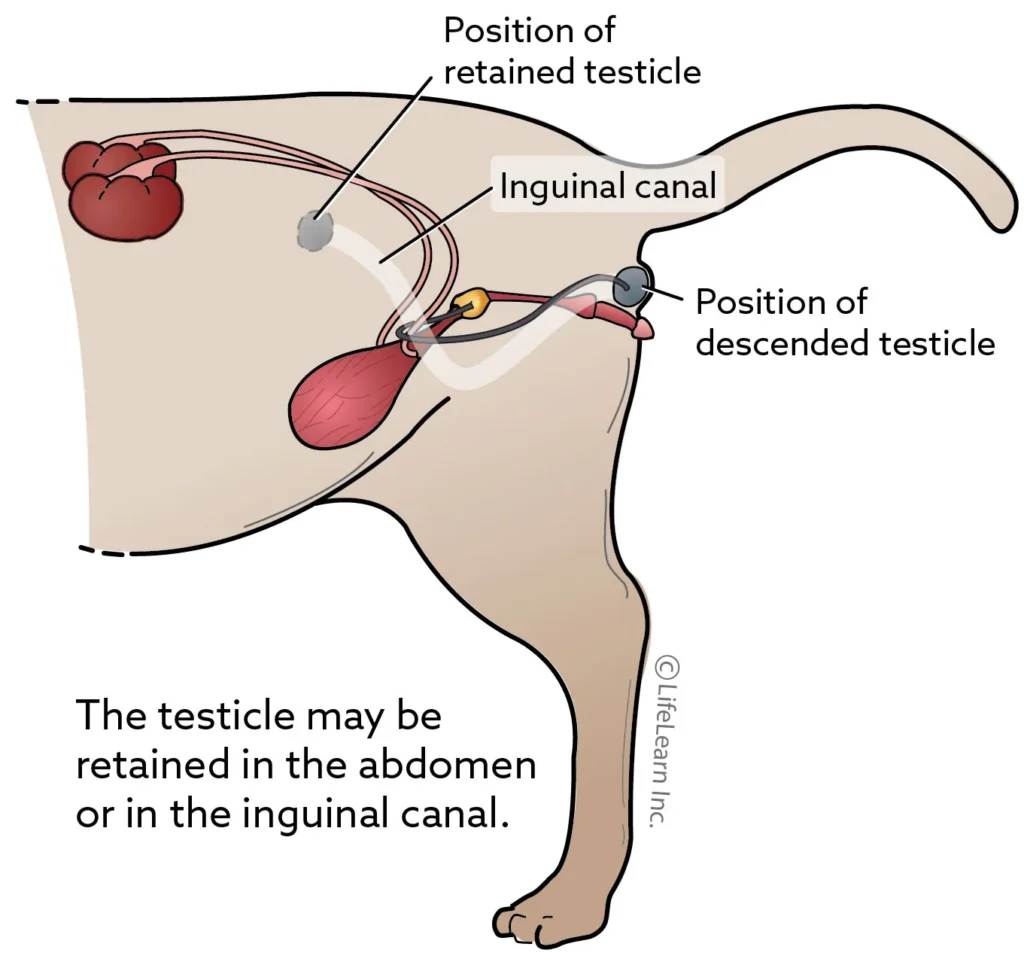
Cryptorchidism is the failure of one or both testicles to descend into the scrotum. Some purebred cats are more at risk, but it can affect any cat and is believed to be an inherited trait. Diagnosis can usually be made by palpation but sometimes requires blood testing or abdominal ultrasound if the cat’s history is unknown. Risks of retained testicles include testicular cancer, spermatic cord torsion, and the development of undesirable male characteristics, so neutering is strongly recommended. Surgery is generally routine, and recovery is similar to any abdominal surgery.
Raising Kittens

Most cats care for their kittens with little need for human intervention; if they do not, then their caregivers need to step in. It is critical to maintain a warm environment and ensure they receive enough milk. Kittens’ weight should be checked daily in the first two weeks and any prolonged crying should be investigated. Feeding can be supplemented with commercial milk replacer if needed. Further feeding and vaccination recommendations are discussed. Contact your veterinarian for specific instructions.
Pyometra in Cats
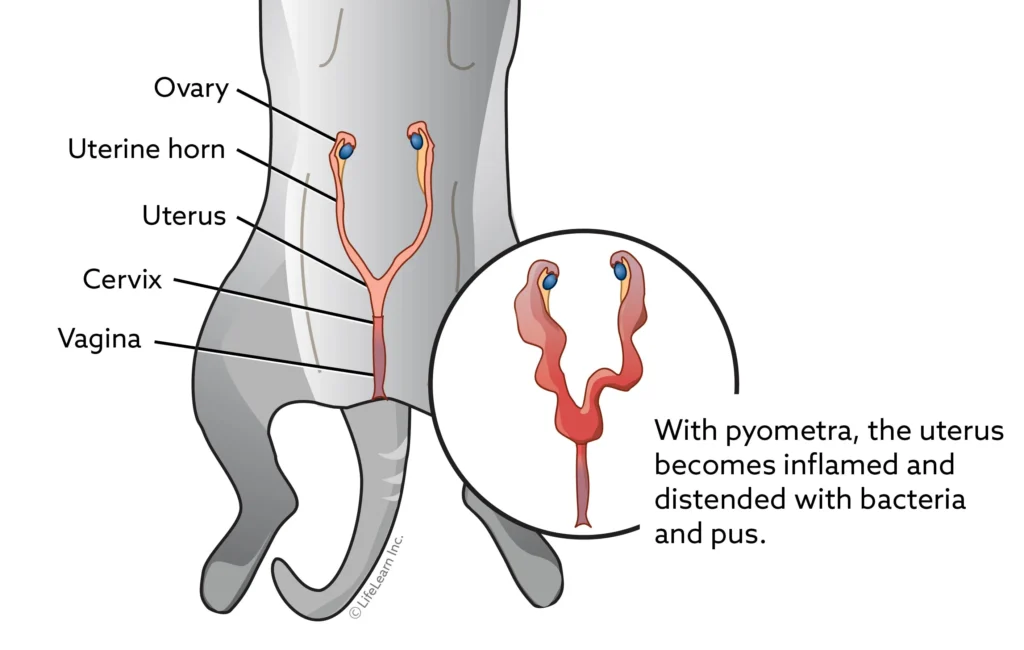
Pyometra is a serious and life-threatening infection in the uterus, occurring in female cats who have not been spayed. The condition must be treated quickly and aggressively. The preferred treatment is to surgically remove the uterus and ovaries by performing an ovariohysterectomy. There is a medical approach to treating pyometra, although the success rate is highly variable and not without considerable risk and potential long-term complications.
Pregnancy Concerns in Pets

Although uncommon, cats and dogs are at risk for several diseases during the two months of their pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia occurs if the mothers cannot keep up with the demand for calcium to produce bones and milk. Gestational diabetes can occur due to high concentrations of hormones and result in increased drinking, urination, inappropriate weight loss and lethargy. Mastitis is a bacterial infection of one or more mammary glands that is contracted either through the blood (sepsis) or from the external environment from unsanitary conditions and/or injury from babies’ teeth or nails. Retained placentas can occur and will result in lethargy, pyrexia and abnormal vulvar discharge. Be aware of the signs, symptoms and management for all four conditions.

