Bile Acid Test

Bile acids are compounds that are made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder and help with digestion of foods. The bile acid test is a very useful test that helps to determine if the liver is working properly. An abnormal bile acid test result indicates there is a problem in the liver, but it does not provide information about the cause, severity, or reversibility of the problem. Further testing is required to investigate the problem.
Arthroscopy

This handout discusses arthroscopy, the insertion of a telescope-like camera into a joint. The joints commonly examined and treated using this technique, along with the benefits and risks of this procedure, are outlined.
Antibody Titers

Antibody titers are sometimes needed to diagnose disease. Antibody titers reflect the level of antibody that the pet has made in response to exposure to a certain infectious organism. The titer is determined by sequentially diluting the serum and testing it against the organism in question. The more dilute the serum when it stops producing a positive reaction, the higher the concentration of antibodies present in the blood. Titers give support to a diagnosis, allowing more targeted treatment and more specific prognostic information, as well as identifying zoonotic disease (diseases transmissible between animals and humans).
Preventive Healthcare Guidelines for Cats

The American Animal Hospital Association and American Veterinary Medical Association have established guidelines to standardize preventive health care for cats, helping them to live longer, healthier lives. This handout provides an overview of the recommendations within these guidelines and why they are so important.
Plaque and Tartar Prevention in Cats
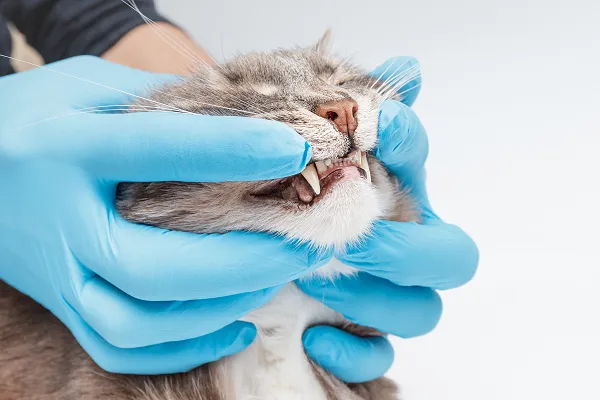
Plaque forms on teeth shortly after eating and within 24 hours begins to harden, eventually turning into tartar. Tartar serves as a place for bacteria to grow, leading to gingivitis. As gingivitis worsens, periodontal disease develops, which includes inflammation, pain, and tooth loss. Prevention of plaque and tartar build-up is key. Use VOHC-accepted food and/or water additives, wipe or brush your cat’s teeth daily, and have your veterinarian perform regular dental cleanings.
Persistent Deciduous Teeth (Baby Teeth) in Cats

A persistent tooth is a deciduous (baby) tooth that is still present when the permanent tooth erupts. When this happens, the baby tooth occupies the place in the mouth that is meant for the permanent tooth, forcing the permanent tooth to erupt at an abnormal angle or in an abnormal position. The result is crowding or malposition of the tooth, causing an abnormal bite (malocclusion). Early extraction is advised.
Orthodontics (Moving Teeth) in Cats
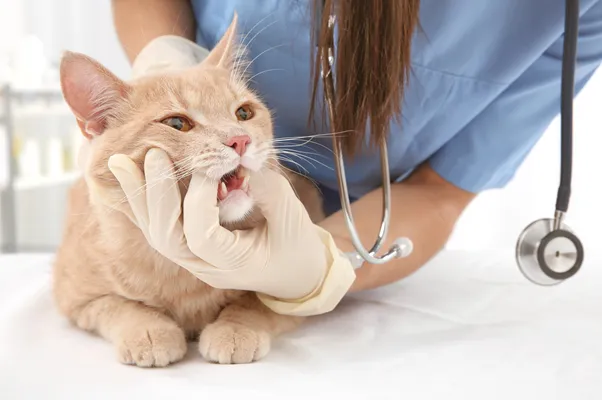
Occasionally, cats’ teeth do not erupt in the right location, resulting in pain and poor function. Treatment options include orthodontic appliances to move the teeth, extraction, or crown amputation with restoration. Many veterinarians are comfortable delivering orthodontic care for cats. Your veterinarian may seek the advice of a board-certified veterinary dental specialist for advice or referral.
Oral Tumors in Cats – An Overview

The most common oral tumor seen in cats is squamous cell carcinoma; the second most common is fibrosarcoma. This handout discusses the clinical signs, diagnosis and treatment of oral tumors in cats.
Oral Tumors in Cats – Fibrosarcomas
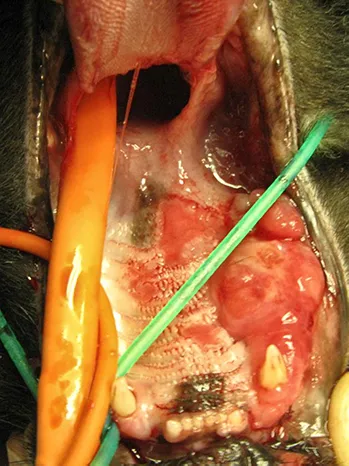
Fibrosarcomas are the second most common oral tumor in cats and arise from the fibrous and connective tissues of the oral cavity. These tumors are very invasive locally and are often difficult to manage, Diagnosis is based on biopsy and treatment involves surgery and occasionally radiation or chemotherapy. Palliative care with pain relief and antibiotics are essential to improve quality of life.
Oral Swellings in Cats
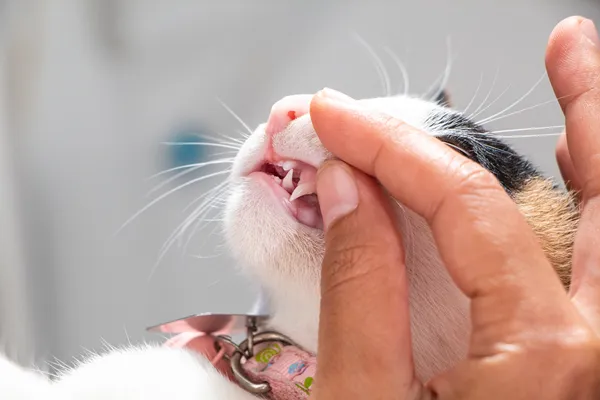
There are many causes of oral swellings, including local trauma, infection, fluid accumulation and tumors. If you find an oral swelling in your cat’s mouth, book an appointment with your veterinarian as soon as possible. Your veterinarian will perform diagnostic tests such as intraoral X-rays, blood tests, and tissue sampling. Treatment and prognosis depend on the cause.

