Cephalexin

Cephalexin (brand names Rilexine®, Keflex®, Vetolexin®) is an oral antibiotic used to treat pyoderma and other bacterial skin infections in dogs and is used off-label in cats to treat pyoderma and other types of skin infections. It is sometimes used off-label to treat urinary tract infections in cats and dogs. Side effects of cephalexin are rare and usually mild.
Caring for Your Sick Cat

When your cat is being treated for an illness, it is important that you follow your veterinarian’s advice and instructions precisely. Take your cat for re-examination requested. If your cat’s condition worsens unexpectedly, contact your veterinarian for advice immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment provide the best outcome for your cat’s recovery.
Care of Open Wounds in Cats
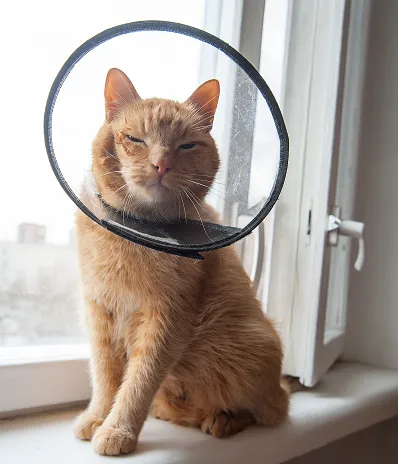
Sometimes, the location of your cat’s wound or the amount of skin lost can prevent surgical closure or bandaging. This handout describes general guidelines for proper care of your cat’s open wound at home, though your veterinarian can provide you with specific instructions.
Biological Response Modifiers

Biological response modifiers (BRMs) are naturally occurring substances that are used to treat diseases, infections, or chronic itchiness or pain, by affecting the immune system and how it works. They are mostly used to treat some cancers, immune-mediated diseases, and infections. Most BRMs are administered in the hospital under veterinary supervision. Side effects vary but may include fever, stomach upset, tiredness, or allergic reactions.
Cruciate Ligament Rupture in Cats

This handout outlines cruciate ligament rupture, an orthopedic condition, in cats. The common causes, clinical signs, diagnosis, and treatments are described.
Corneal Ulcers (Ulcerative Keratitis) in Cats

Ulcerative keratitis is inflammation in the cornea of the eye. The signs of ulcerative keratitis depend somewhat on the cause and how long the condition has been present. There are many potential causes of ulcerative keratitis, including trauma, infection, and abnormal tear production. Antibiotic ointment or drops will be prescribed and it is important to prevent additional trauma to the cornea. Superficial corneal ulcers typically heal within 5 to 7 days. Deeper or more complicated ulcers may take several weeks to heal and may require surgery in addition to medical treatment.
Cholangitis/Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome in Cats

Cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis in cats refers to inflammation of the bile duct or a combination of inflammation of the bile duct, gallbladder, and surrounding liver tissue. The clinical signs, diagnosis, treatments, and prognosis of the conditions are outlined in this handout.
Cataracts in Cats

A cataract is an increase in opacity of the eye’s lens. Any type of inflammation or damage to the lens can lead to a cataract. The clinical signs of cataracts vary depending on the size of the cataract; many cataracts are asymptomatic at the time they are diagnosed during a veterinary exam. The ideal treatment for cataracts is surgery, but not all cats are candidates for surgical treatment. In these cases, anti-inflammatory medications may be used to prevent glaucoma and other secondary complications of cataracts.
Care of Surgical Incisions in Cats
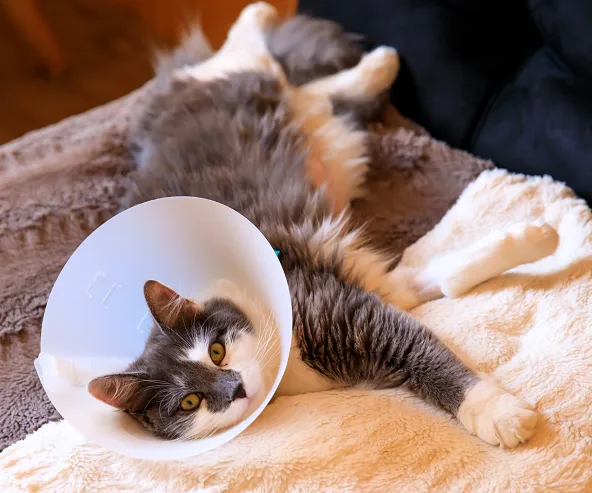
The general instructions for incision care are the same for all surgical incisions. There may be some differences, however, depending on the type of surgery and the material used to close the incision. This handout is a guide to caring for your cat’s surgical incision(s) at home for optimal recovery.
Calcium Oxalate Bladder Stones in Cats

Calcium oxalate bladder stones are composed of a mineral called calcium oxalate. Cats are more likely to develop oxalate stones when their urine contains high levels of calcium and oxalate. Additionally, a low urine pH promotes the formation of oxalate stones. Bladder stones can cause significant inflammation and irritation of the bladder wall. Signs may include frequent urination, straining to urinate, blood in the urine, and urinating outside of the litterbox. Male cats especially are at risk of a life-threatening urinary obstruction. Treatment options and prognosis are discussed.
