Diabetes in Cats: Testing and Monitoring

Testing for diabetes includes confirming hyperglycemia and glucosuria while looking for other conditions by taking a complete blood count (anemia, infection), biochemistry profile (hepatic disease, pancreatitis), and a urinalysis (urinary tract infection). Monitoring includes regular glucose curves and additional exams and testing based on the pet owner’s monitoring of their cat’s clinical signs at home. Urine glucose testing and fructosamine are sometimes used in diabetic monitoring and urine testing for infection may be recommended.
Dexamethasone Suppression Tests

Dexamethasone is used to test the level of cortisol hormone in the body. Injection of dexamethasone will cause a decreased level of cortisol in a normal pet; however, in a pet with Cushing’s disease, there is minimal or no decrease in cortisol level. Other diseases can suppress cortisol production, so it is important to rule these out prior to dexamethasone testing. Knowing the type of Cushing’s disease your pet has can guide treatment decisions and offers a more defined prognosis.
Cytology – Collecting Cells from Surfaces

Cytology is the microscopic examination of cells that have been collected from the body. Lesions on the surface of the skin or from moist body cavities can be sampled very simply by scraping, swabbing, flushing, or making impressions of the tissue. The collected cells get looked at under a microscope and in many cases a diagnosis can be made to determine the best form of treatment.
Cytology – General

Cytology is a useful tool to often diagnose abnormal lumps on your pet’s body as well as evaluation of fluid samples and tissue surfaces. It is relatively simple and inexpensive but can provide a lot of information. Depending on results, further tests may be indicated to best help your pet.
Coombs’ Test
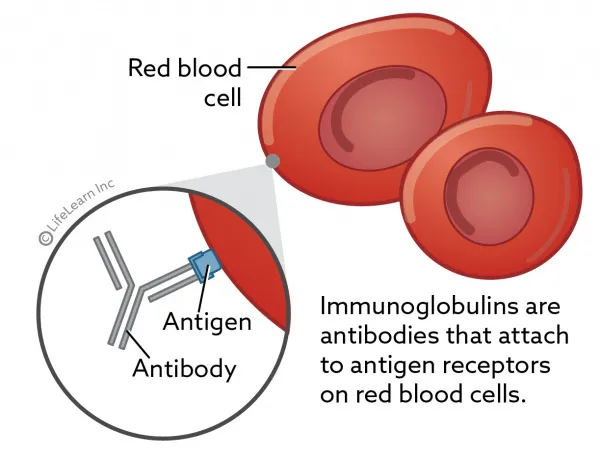
A Coombs’ test is used to test for a disease called autoimmune hemolytic anemia (IMHA). IMHA is a condition where the immune system breaks down or destroys red blood cells, leading to anemia. The test detects the presence of immunoglobulins (antibodies) on the surface of red blood cells. Taken together, the physical findings and the laboratory data (such as a Coombs’ test) may suggest that immune-mediated destruction of red blood cells is the most likely cause of your pet’s anemia.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)

The complete blood count (CBC) assesses different parameters of the cells in the blood including total number, appearance, size, and shape. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets comprise the cellular component of the blood.
Coagulation Tests
Coagulation is the series of events that result in the formation of a clot. In the body, coagulation occurs after any injury to a blood vessel or tissue, in order to stop the bleeding. Certain diseases such as liver disease and rodenticide toxicity can affect the production of clotting factors.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Collection and Examination
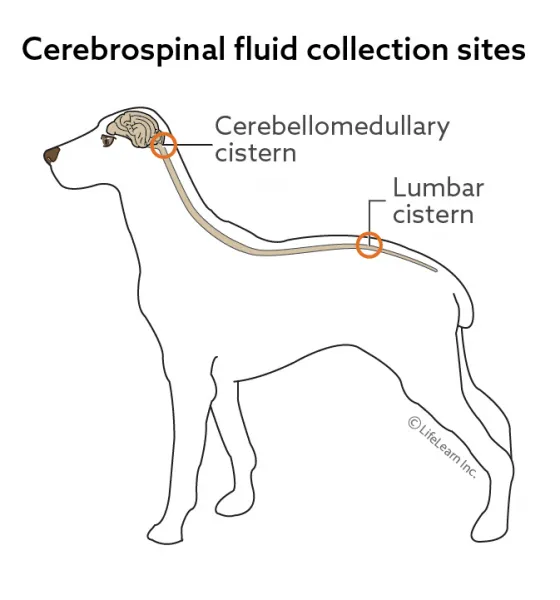
Cerebrospinal fluid is a clear, colorless fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. The collection of CSF is usually indicated when a pet shows clinical signs, such as seizures, incoordination, circling behavior, and neck or back pain, when no obvious cause is known. The veterinary pathologist will evaluate the sample for a total nucleated cell count, a red blood cell count, a total protein determination, and a concentration of the cells in the sample. The presence of bacteria or fungal organisms may be detected along with increased numbers of inflammatory cells, leading to a diagnosis of bacterial or fungal infection. Neoplastic cells may also be found, indicating an underlying tumor within the brain or spinal cord.
Buffy Coat Examination for Mast Cells
The fastest way to examine large numbers of white blood cells is to look at a buffy coat smear. One of the most important cells to look for in a buffy coat is called a mast cell. Mast cells play an important role in allergies and related conditions.
Bone Marrow Collection and Examination

Bone marrow is the soft material found in the central core of many bones. Bone marrow is commonly collected and examined when abnormalities are found in the circulating blood. The pathologist’s report typically provides information about the health of the marrow, the types of cells present, whether abnormal cells are found, and other details that may help to explain the patient’s illness.

